|
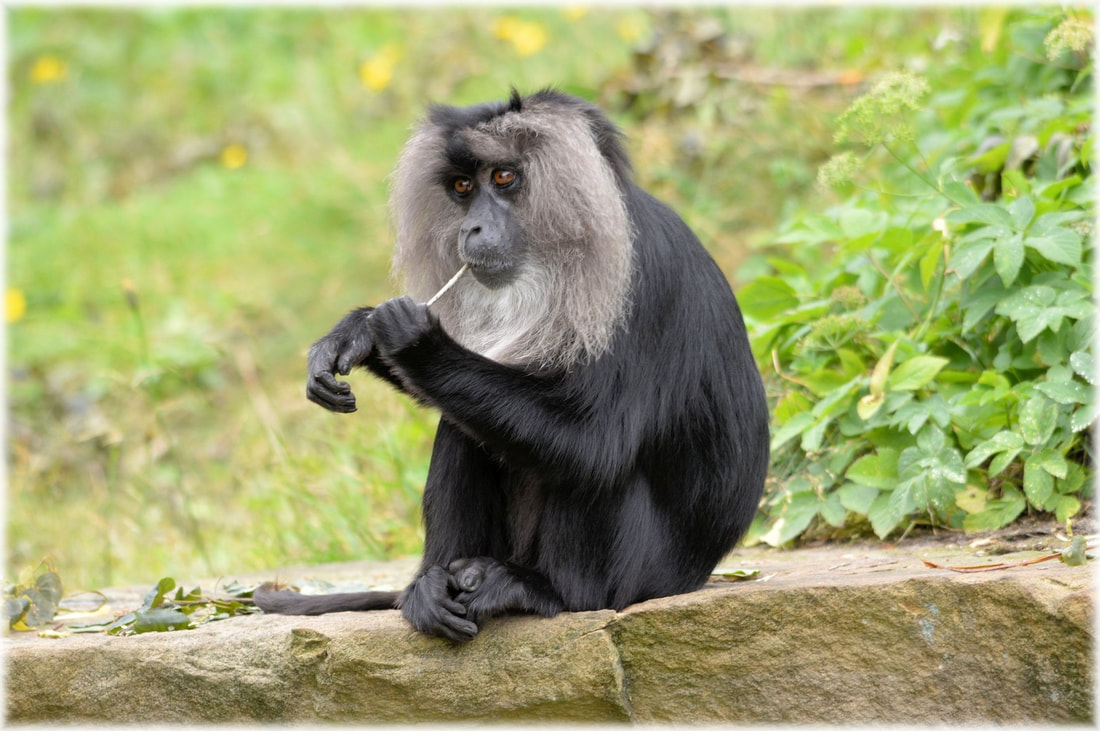
Lion-tailed macaques are an endangered species of primates found only in the Western Ghats of India. With a population of fewer than 2,500 individuals (based on IUCN Red List), these charismatic animals are threatened by habitat loss, hunting, and fragmentation of their forested habitats. However, conservation efforts are underway to save these macaques from extinction, and one of the keys to their success has been collaboration and community involvement. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of collaboration and community involvement in lion-tailed macaque conservation and how these efforts are making a difference in the survival of this endangered species. The lion-tailed macaque (Macaca silenus) is an endangered species found only in the Western Ghats of India. As such, it is important to identify the most suitable stakeholders for its conservation and protection. Here are three stakeholders that would be crucial for the well-being of the lion-tailed macaque:
Here are some examples of specific stakeholders relevant to the conservation of the lion-tailed macaque in India:
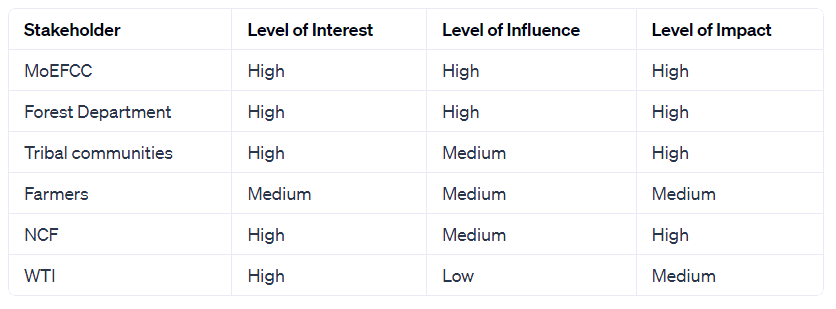
For each stakeholder, we can assess their level of interest, influence, and impact on the project. Here's an example of how we can assess the stakeholders using a matrix: But why?
Here's a brief explanation of my choices for each of the stakeholders:
|